Learn About Cannabis
Cannabis is a beautiful, amazing plant that many rely on for potential health and well-being benefits. The natural elements of cannabis are complex and fascinating, with the ability to construct thousands of cannabinoid and terpene combinations.

Did you know that the human body is naturally equipped to receive healing benefits from the cannabis plant? Read on to learn how the cannabis plant and it’s naturally secreted elements play a role in the many reported therapeutic benefits.
Learn how your body is naturally equipped to utilize the cannabis plant’s therapeutic benefits.
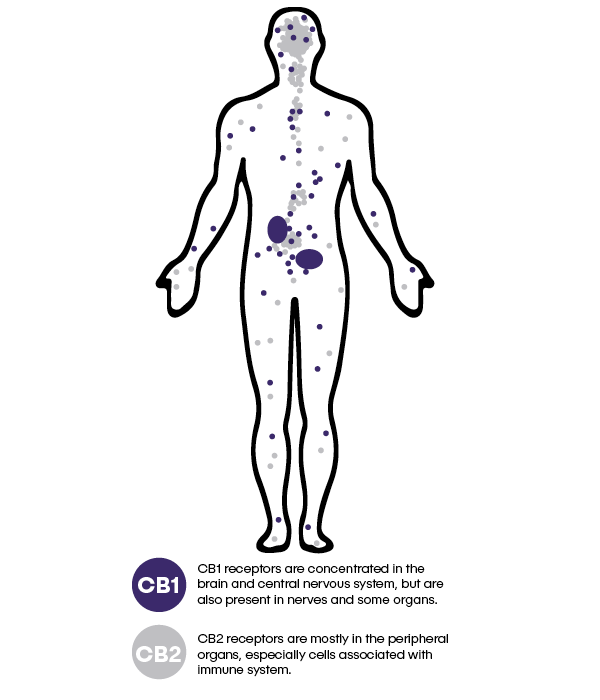
The Human Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a biological system found in all mammals, and is involved in managing a wide variety of biological processes, including memory, sleep, immune response, and more.
It mainly consists of two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).
These receptors are built to interact with endocannabinoids (cannabinoids naturally produced by the brain).
They can also interact with plant-derived cannabinoids, which in turn cause a variety of responses throughout the body.
Cannabinoids have demonstrated potential for a wide spectrum of therapeutic uses, including: antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory , anti-pain, anti-tumor, sleep modulating effects, anti-psychotic and anti-anxiety.
The most well-known delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is responsible for the “high” of cannabis and can affect perception, mood, emotion, cognition, and motor function.
There are also numerous cannabinoids, like cannabidiol (CBD), which are non-psychoactive yet have medically useful properties.
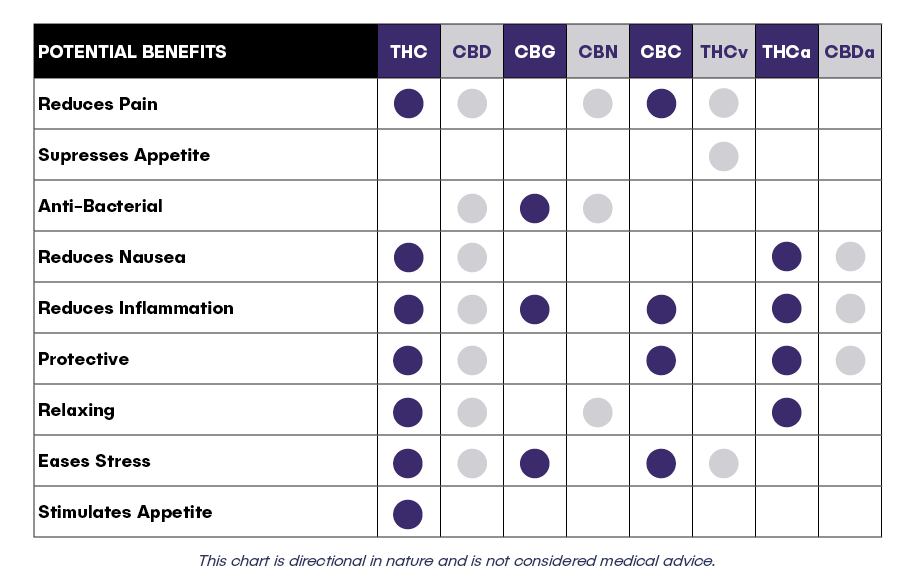
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds secreted by cannabis flowers that interact with receptors in the brain to provide relief to an array of symptoms including pain, nausea, anxiety, and inflammation.
Although all cannabinoids play an important role in providing relief for qualifying conditions and symptoms, the two most popular cannabinoids are THC and CBD.
When cannabis is consumed, cannabinoids bind to receptor sites throughout our brain (receptors called CB-1) and body (CB-2). Different cannabinoids have different effects depending on which receptors they bind to. For example, THC binds with the CB1 receptors in the brain, which are found mainly in our central nervous system. Their activation has cerebral and behavioral effects which also produces a high or sense of euphoria. CBD binds with the CB2 receptors, mostly in the peripheral nervous system and associated with the immune system and inflammation response. Activating the CB2 can relax the body, help it repair itself and reduce the sensation of pain without impairing cognition.
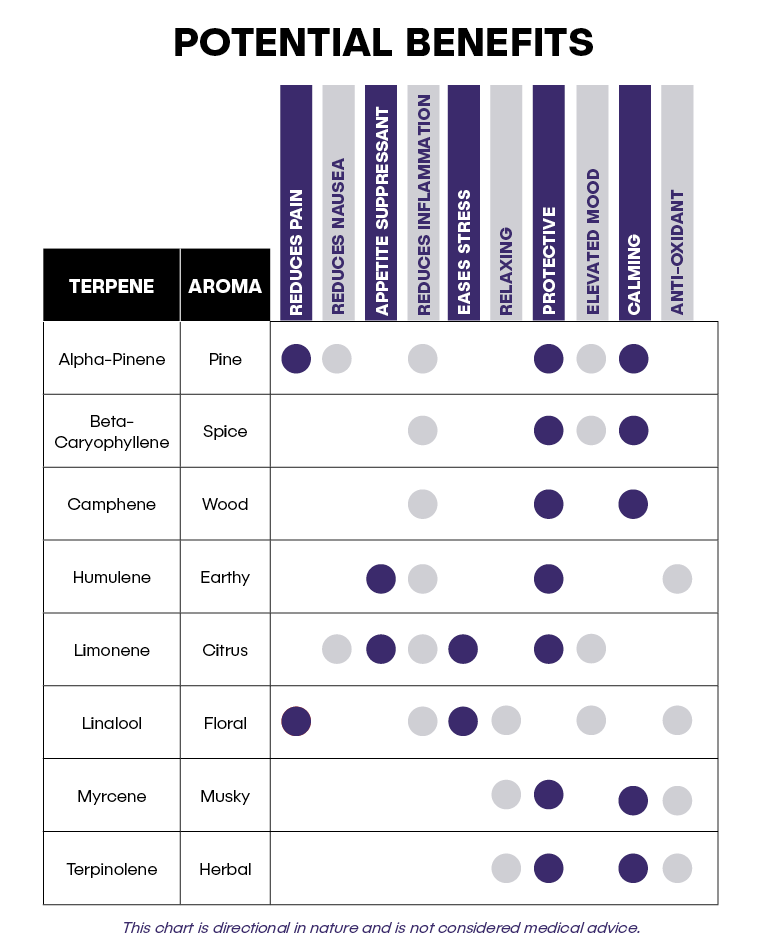
Secreted in the same glands that produce cannabinoids like THC and CBD, terpenes are aromatic oils that play a key role in differentiating the effects of various cannabis strains.
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in many plants that are responsible for the plant’s characteristic scents (think: linalool in lavender, and limonene in orange). Some terpenes play a protective role, both in the plant and when consumed.
The 6 most commonly found terpenes are Limonene, Humulene, Pinene, Linalool, Caryophyllene and Myrcene. Use this resource to help determine which products will create your desired effects.
Each cannabinoid and terpene has its own set of therapeutic benefits and unique properties, and when consumed together they can enhance each other’s effects.
In this way, they are more effective together than if they are alone. This is referred to as the “Entourage Effect”.
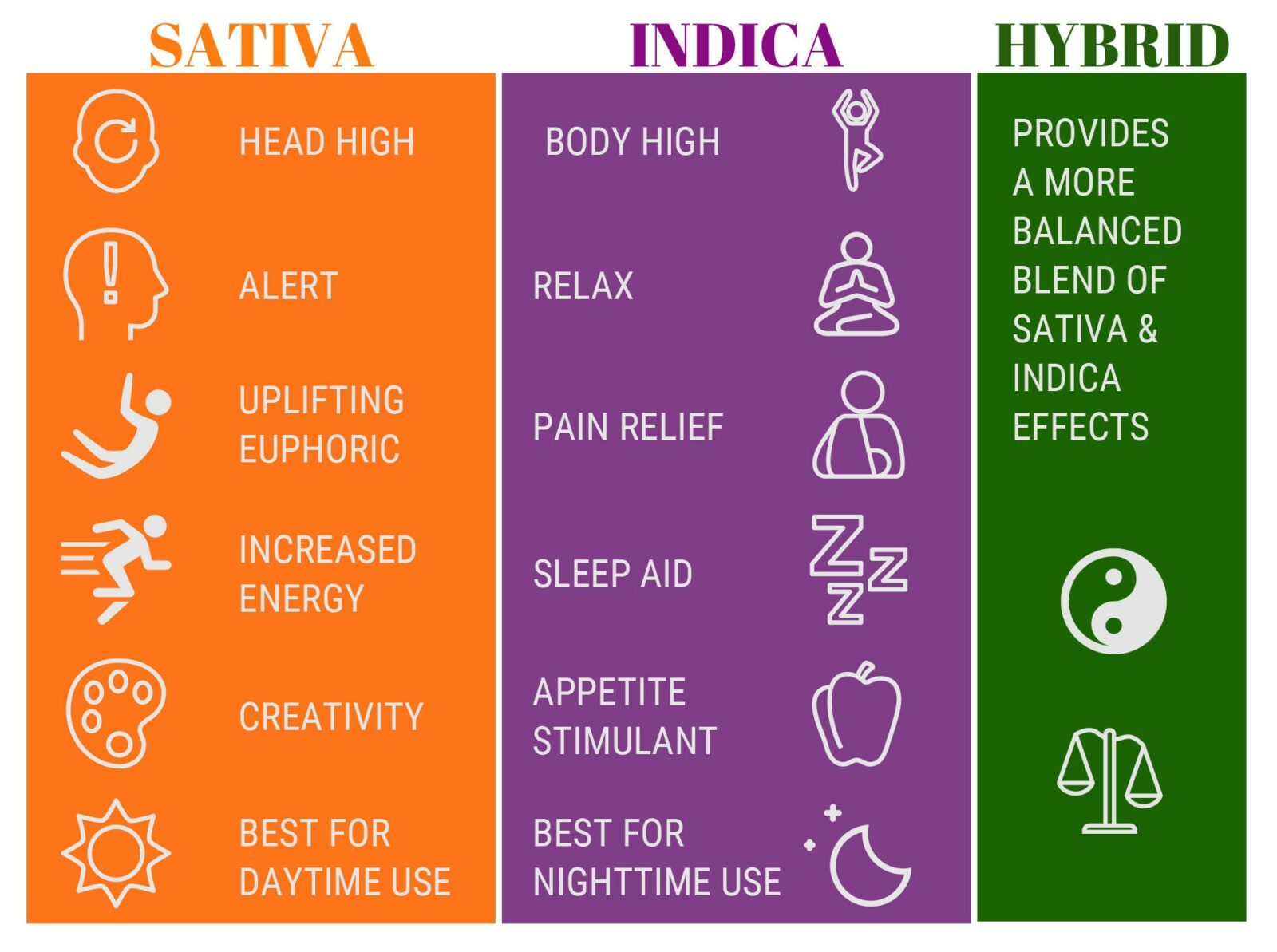
Cannabis strains are historically sorted into three categories: Sativa, Indica and Hybrid. Each strain has it’s own range of effects on the body and mind, resulting in a wide range of medicinal benefits.
-
Sativas are said to provide invigorating, uplifting cerebral effects that pair well with physical activity, social gatherings, and creative projects.
-
Indica strains are known to be physically sedating, perfect for relaxing with a movie or as a nightcap before bed.
-
Hybrids are thought to fall somewhere in between, offering a balance of indica and sativa effects.
While the strain can be a great start to determining which cannabis products are best for you, it is also important to know which cannabinoids and terpenes are present. Ultimately, the combination of all of these properties is what will form the desired effects.
When consuming cannabis, one of the most important factors is the delivery method. With advances in product innovation, products are available to inhale, ingest, absorb, and apply on your skin. Each method offers different dosage types and is crafted for different purposes. Talk with your certified pharmacist to see which method would be best for you.
INHALATION: Vaporized Flower, Oils & Extracts
When cannabis is inhaled, the gases enter the lungs before absorbing into the bloodstream. A vaporizer produces a stream of vapor (not smoke) that is inhaled.
SUBLINGUAL: Tinctures & Sprays
Tinctures and sprays are a liquid cannabis extract used by consumers looking for dosage control and fast-acting effects without the health risks associated with smoking. You can find tinctures with varying levels of THC per dose.
TOPICAL: Patches, Salves, Lotions & Oils
Topical effects differ from other methods in that anecdotal evidence suggests that they don’t provide the cerebral stimulation that users describe as “being high.” Because of this, topicals may be appropriate for consumers needing a clear head and localized relief (for example, muscle aches or soreness).
ORAL INGESTION: Capsules & Edibles
Eating or drinking cannabis provides significantly different effects from other delivery methods that immediately enter the bloodstream. It has been reported that orally ingested products have longer onsets and tend to cause powerful full-body, psychoactive effects depending on dosage.